Understanding the Recent Surge in Renewable Energy Adoption
Table of Contents
The global energy landscape is witnessing a transformative shift as renewable energy sources become more prevalent. In recent times, the surge in the adoption of renewable energy has garnered significant attention from policymakers and industries alike. But what is driving this change, and what implications does it hold for the future?
The Factors Driving Renewable Energy Adoption
Environmental Concerns
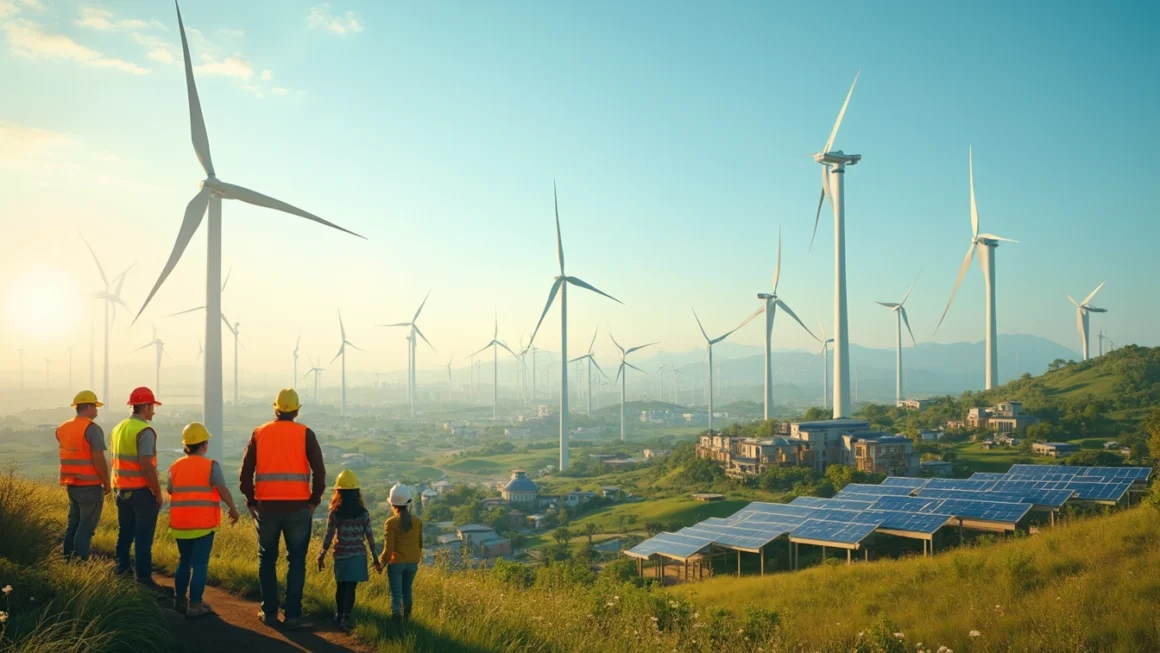
One of the primary catalysts for the shift towards renewable energy is growing environmental concerns. As awareness of climate change increases, there is a substantial push to reduce carbon footprints and reliance on fossil fuels. This trend is visible across nations, with stringent regulations and incentives to promote green energy.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology have also played a pivotal role in the renewable energy boom. Breakthroughs in solar panel efficiency and cost reductions in wind energy production have made these options more viable and competitive with traditional energy sources. As technology continues to advance, the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy are expected to improve further.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
The economic implications of renewable energy adoption are vast. Investing in renewables is not only environmentally sound but also economically advantageous. Renewable energy projects have been shown to create more jobs compared to fossil fuel projects. This factor is crucial for economic recovery, especially in regions hit hard by economic downturns.
The Implications for Future Energy Grids
The shift towards renewable energy signifies a fundamental change in energy grid management. Energy grids are becoming more decentralized, allowing for a larger integration of distributed energy resources. This transition requires upgrading infrastructure to accommodate renewable sources and ensure grid stability.
Challenges in Grid Management
While the benefits of renewable energy are clear, integrating these sources into existing grids poses certain challenges. Issues such as energy storage, maintaining supply reliability, and managing energy flows require innovative solutions.
Solutions and Innovations
To overcome these challenges, innovations such as battery storage systems and smart grid technologies are being developed. These systems enhance the ability to store excess energy and efficiently distribute it during peak demand times. Additionally, they help optimize grid operations and improve resilience.
The Role of Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives are crucial in driving the adoption of renewable energy. By providing subsidies for green technologies, enforcing emissions targets, and investing in research, governments can significantly accelerate the transition towards sustainable energy solutions.
Global Efforts and Cooperation
International cooperation and agreements play a significant role in this transition. Events like the Paris Agreement have set ambitious targets for reducing global emissions, pushing countries to adopt more renewable energy solutions. Collaboration among nations ensures a unified and effective approach to tackle climate-related challenges.
Conclusion: A Renewable Future
In conclusion, the global movement towards renewable energy is largely driven by environmental, technological, and economic factors. The transition presents opportunities for sustainable growth, job creation, and technological innovation, albeit with certain challenges. As the world navigates this change, it becomes imperative to focus on adaptable policies, enhance energy grids, and promote global cooperation to foster a stable and renewable energy future.
To explore more on sustainable practices and technological advancements, visit this portfolio website.